All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
The Best Double Glazing Companies In Canberra in Osborne Park Perth
That window can send more solar heat in winter season than in summer season. A west-facing window on a summer's afternoon has an angle of occurrence from near 0 as much as 30 with a big reliable location of solar radiation. A north-facing window, in summertime, has a high angle of occurrence and a low effective area of solar radiation, so can transfer less heat than a west-facing one.
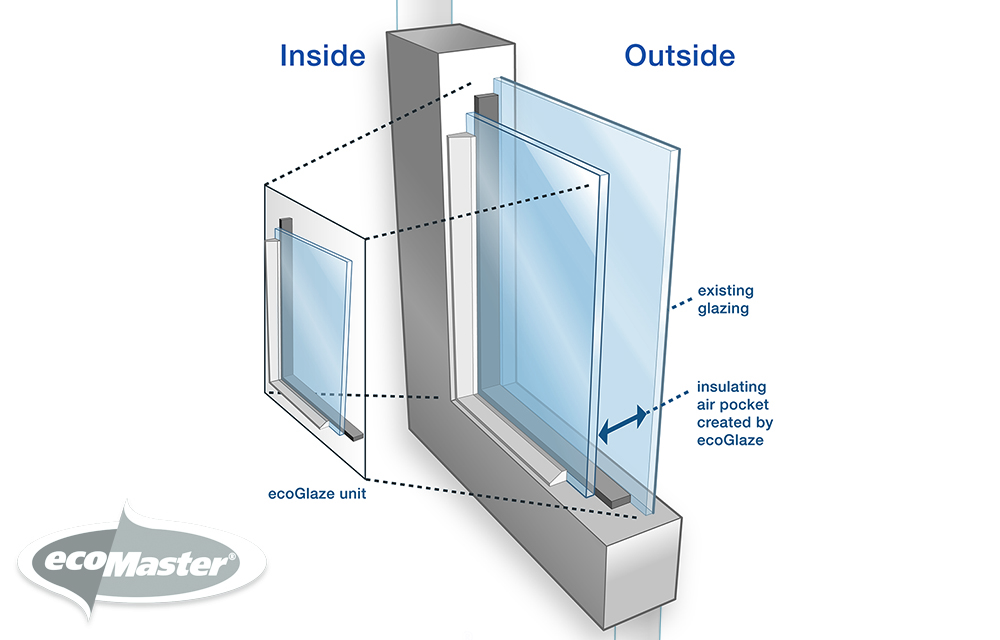
You can quickly and quickly improve the thermal efficiency of your home by changing your windows. There are thousands of types of glass and frames to choose from.
Climateframe Double Glazing: Perth's Double Glazed ... in Bayswater Perth
Single glazing with clear glass is not extremely efficient when it comes to heat loss or gain. To enhance efficiency, you can use single glazing with a more energy-efficient type of glass such as low emissivity (low-e) glass.
Several layers can be assembled with sealed cavities in between each sheet of glass. IGUs usually use better energy efficiency than single glazing, since they transfer less energy. However, the energy performance of IGUs likewise depends on: the residential or commercial properties of each layer of glass. Various glass types (for example, clear and low-e glass) can be assembled in an IGU.
Carnegie 3163, Vic. Amazing Service By Aps Double Glazing in Clarkson Western Australia

IGU cavities can be filled with air or a more inert, low-conductivity gas such as argon the width of the cavity. Larger cavities offer lower (better) U worths, with 12mm normally accepted as the preferred gap how well the cavity is sealed.
If argon is installed to the cavity in location of air, moisture is dependably omitted the level of desiccant (drying agent). The spacer (metal or polymer strip) that separates the glass layers consists of a desiccant to take in any wetness. Insufficient desiccant might cause moisture to condense on the glass surface in cold conditions, decreasing thermal efficiency.
Improve Your Home's Energy Efficiency With Double Glazing in Joondalup WA
IGUs can deliver much better energy efficiency for all environments, specifically in heated and air-conditioned houses. Cross-section detail of single, double and triple-glazing systems Low emissivity glass (typically called low-e glass) lowers heat transfer. Low-e glass may be either high or low transmission: High transmission low-e glass has a covering that permits daylight from the sun to enter your home to achieve good solar heat gain, however minimizes the amount of the long wavelength infrared heat that can leave back through the window.
Low-e glass has either a pyrolytic finishing or a vacuum-deposited thin movie metal finish. Pyrolytic coatings are resilient and can be utilized for any glazing; vacuum-deposited finishings are soft and are only utilized within IGUs. Low-e coatings can considerably improve both U value and SHGC; nevertheless, they should be utilized properly or they will either deteriorate or fail to carry out as required.
Double Glazing For Warmer Temperature : R/melbourne in Wandi Western Australia
Low-e finishes can be utilized in combination with clear, toned or reflective glass. Low-e coatings on glazing can lower heat transfer where required Image: Department of Industry, Science, Energy and Resources Toned glass has colouring additives included during manufacture. It is readily available in numerous colours, normally bronze, grey, blue and green.
Latest Posts
Double Glazed Windows: A Complete Guide in Kelmscott WA
How Does Double Glazing Keep Heat Out? in Lathlain Western Australia
A Complete Guide To Double Glazed Windows in Wembley Downs WA